It is a system of digital documents authentication similar to the paper signature and it is based on cryptography with asymmetric keys. The process of digital signature [I1] [I2] [I3] [F1]
[F2] [F3]
[S1]
[S2]
[S3]
[E1] [E2] consists into three phases:
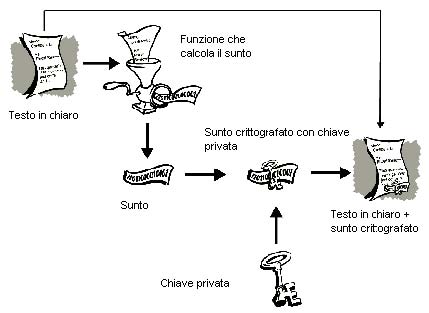
- a particolar function is applied on the clear text. It calculates the summary of the message
- the obtained summary is ciphered with its own private key
- the clear message is sent to the sender together with the summary signed with the senderís private key.
The addressee receives the clear message and the summary of the message sent by the sender. In order to verify that the message is not altered and comes exactly from the chosen person, the addressee must:
- apply the senderís public key to the signed summary to verify that it comes from the real sender (obtaining in this way the clear summary)
- calculate again the summary† of the clear message with the mathematic function †obtaining by this way a second summary
- verify that the previous calculated summary and the one sent by the sender are the same. If so the message has not been modified.