An algorithm is based on an asymmetric cryptography [I1] [I2]
[F1] [F2] [S1] [E1] [E2] [E3] [E4] if the key it uses to code is different from the key used to decode. It is asymmetric because the symmetry occurring on algorithm based on private key does not exist. It is asymmetric because there is a key that allows me to shift from the clear text to the coded one and another key (different from the previous) that allows me the opposite process, that is, from the coded to clear text.
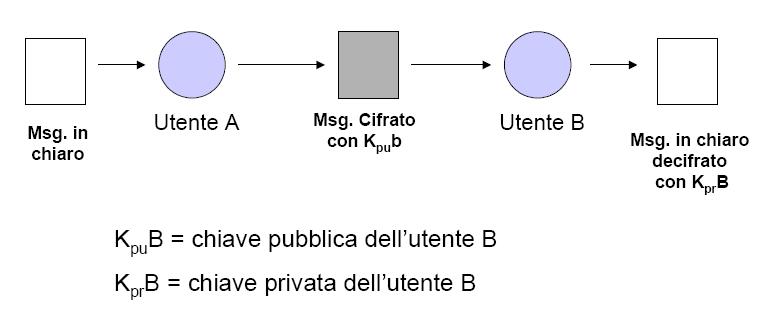
This technique requires two keys to function, so each subject using this technology needs two keys: a private one (that is strictly confidential) and another one, called public key. This last key can be given to anybody.

So each subject has a strictly confidential key and another one that gives to all the people he wants to talk to.

Why do I need two keys and why can I give the public key to everybody? At a first sight it seems that this action can compromise the security of the subject. However it is not like that because the subject has a private key that allows him to make the following operations:

Letís try to understand the functioning of the two keys. First of all remember that if I close the asymmetric lock with a key, I can only open my secret box with the other key and vice-versa. So, If I use the public key to close, I can only open it with the private one. To sum up, this strange lock which is not traditional allows me to create authentication functions and secret functions that we highlighted as basic elements.
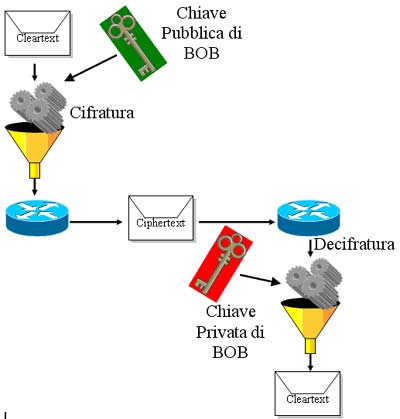
Letís see an example in the following picture. If Alice and Bob want to communicate by using the public key codification, they both need a two public and two private keys. Alice needs to create his pair of public/private keys and so does Bob. When Alice and Bob† have to communicate safely they use different keys to code and decode data. That is, Alice ciphers a message addressed to Bob with Bobís public key and this can only be decoded by the corresponding Bobís private key which I unique and strictly associated to the public one. Bob will cipher Aliceís message with her public key that only Alice will decode with her private key.
Here you have some abbbreviations very popular in Internet to refer to algorithms with asymmetric/public key.
- RSA(Rivest - Shamir - Adleman)
- DSA(Digital Segnature Algoritm)
- Fortezza
- Diffie-Hellman
These algorithms are used in e-commerce to assure safe transactions, that is safe code, password and credit number. They are used furthermore to sign digitally giving the concept of digital signature.
.
